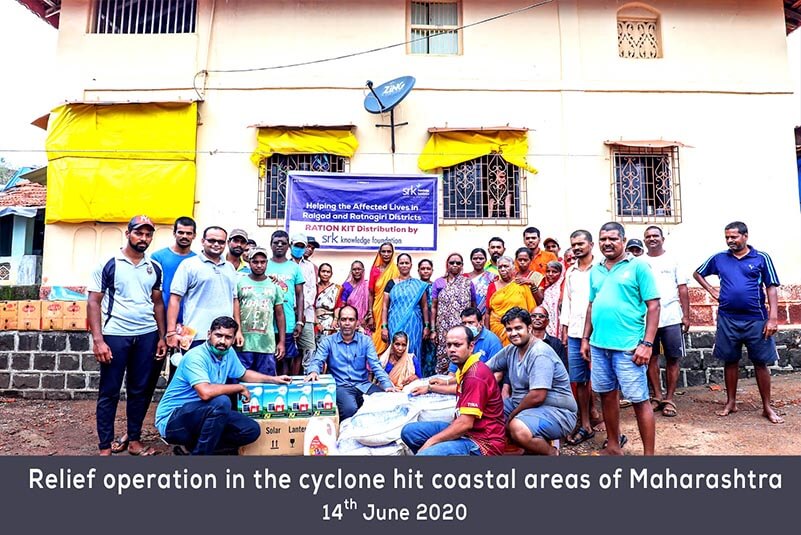
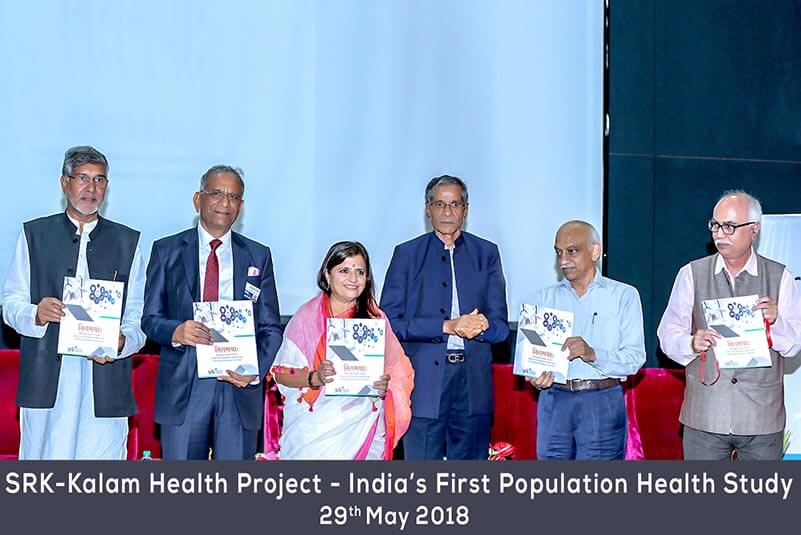
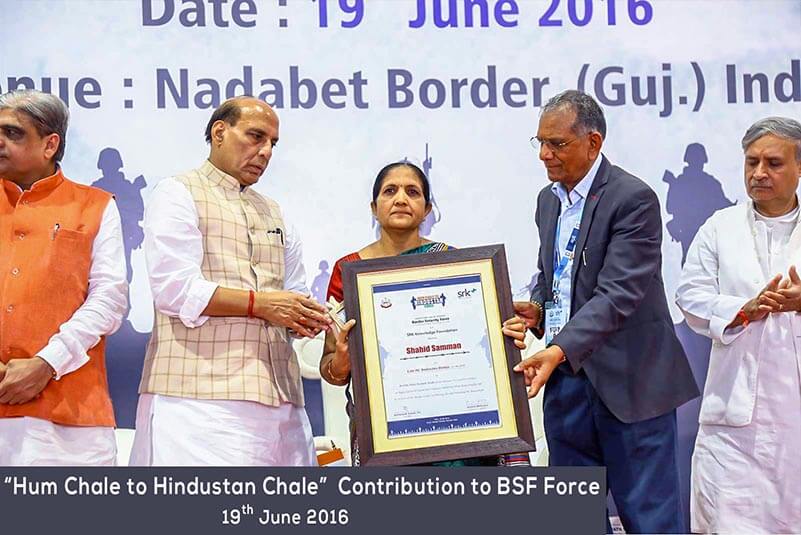
2023
SRK becomes a member of
Natural Diamond Council (NDC).
SRK recognized with South
Gujarat Productivity Council's Award of Excellence!
SRK recognized with 'Green
Innovation Award' and 'ESG Impact Award' during the "National Summit
on ESG2023" jointly organized by Sigma University India.
SRK becomes a member of
World Diamond Council (WDC).
SRK recognized as the
“Stalwart Torch Bearer and Doyen of Futuristic Digitalisation
Adoption in Gujarat’s Business Fraternity” by the GESIA IT
Association on 5th August 2023, at Vadodara, Gujarat.
SRK recognized with the
'Most Preferred Workplace Award' by Marksmen Daily at Mumbai.
Shri Govindkaka recognized
with the 'Lifetime Achievement Award in Philanthropy' by Hurun India
& EdelGive Foundation at Mumbai.
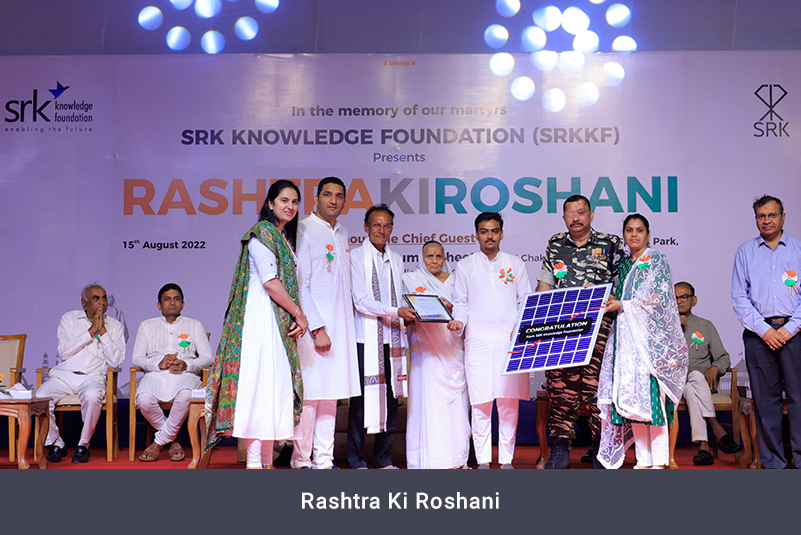
SRK organised
first-of-its-kind ‘SRK Sustainability Conclave 2023’ in the month of
May.
Shri Govindkaka recognized
for 'Outstanding contribution to the diamond industry' at the House
of Lords, London.
SRK recognized with "Hurun
Most Respected Family Business of the Year" by Hurun Report Global
on 2nd February 2023, at Mumbai.
Prof. Marianne Bertrand, The
Chris P. Dialynas Distinguished Service Professor of Economics,
University of Chicago, spoke about ‘Gender, Stereotypes, and
Inequality' during the Fifth Annual IIMA-SRKKF Lecture Series held
at IIM campus, Ahmedabad.